AA搜索算法
引言
1968年,的一篇论文,“P. E. Hart, N. J. Nilsson, and B. Raphael. A formal basis for the heuristic determination of minimum cost paths in graphs. IEEE Trans. Syst. Sci. and Cybernetics, SSC-4(2):100-107, 1968”。从此,一种精巧、高效的算法——AA算法横空出世了,并在相关领域得到了广泛的应用。
启发式搜索算法
要理解AA搜寻算法,还得从启发式搜索算法开始谈起。
所谓启发式搜索,就在于当前搜索结点往下选择下一步结点时,可以通过一个启发函数来进行选择,选择代价最少的结点作为下一步搜索结点而跳转其上(遇到有一个以上代价最少的结点,不妨选距离当前搜索点最近一次展开的搜索点进行下一步搜索)。
DFS和BFS在展开子结点时均属于盲目型搜索,也就是说,它不会选择哪个结点在下一次搜索中更优而去跳转到该结点进行下一步的搜索。在运气不好的情形中,均需要试探完整个解集空间, 显然,只能适用于问题规模不大的搜索问题中。
而与DFS,BFS不同的是,一个经过仔细设计的启发函数,往往在很快的时间内就可得到一个搜索问题的最优解,对于NP问题,亦可在多项式时间内得到一个较优解。是的,关键就是如何设计这个启发函数。
AA搜寻算法
AA搜寻算法,俗称A星算法,作为启发式搜索算法中的一种,这是一种在图形平面上,有多个节点的路径,求出最低通过成本的算法。常用于游戏中的NPC的移动计算,或线上游戏的BOT的移动计算上。该算法像Dijkstra算法一样,可以找到一条最短路径;也像BFS一样,进行启发式的搜索。
AA算法最为核心的部分,就在于它的一个估值函数的设计上:
f(n)=g(n)+h(n)
其中f(n)是每个可能试探点的估值,它有两部分组成:
- 一部分,为g(n),它表示从起始搜索点到当前点的代价(通常用某结点在搜索树中的深度来表示)。
- 另一部分,即h(n),它表示启发式搜索中最为重要的一部分,即当前结点到目标结点的估值,h(n)设计的好坏,直接影响着具有此种启发式函数的启发式算法的是否能称为AA算法。
一种具有f(n)=g(n)+h(n)策略的启发式算法能成为AA算法的充分条件是:
- 搜索树上存在着从起始点到终了点的最优路径。
- 问题域是有限的。
- 所有结点的子结点的搜索代价值>0。
- h(n)=<h(n) (h(n)为实际问题的代价值)。
当此四个条件都满足时,一个具有f(n)=g(n)+h(n)策略的启发式算法能成为AA算法,并一定能找到最优解。
对于一个搜索问题,显然,条件1,2,3都是很容易满足的,而条件4: h(n)<=h(n)是需要精心设计的,由于h(n)显然是无法知道的,所以,一个满足条件4的启发策略h(n)就来的难能可贵了。
不过,对于图的最优路径搜索和八数码问题,有些相关策略h(n)不仅很好理解,而且已经在理论上证明是满足条件4的,从而为这个算法的推广起到了决定性的作用。
且h(n)距离h(n)的呈度不能过大,否则h(n)就没有过强的区分能力,算法效率并不会很高。对一个好的h(n)的评价是:h(n)在h(n)的下界之下,并且尽量接近h*(n)。
AA搜寻算法的实现
先举一个小小的例子:即求V0->V5的路径,V0->V5的过程中,可以经由V1,V2,V3,V4各点达到目的点V5。下面的问题,即是求此起始顶点V0->途径任意顶点V1、V2、V3、V4->目标顶点V5的最短路径。
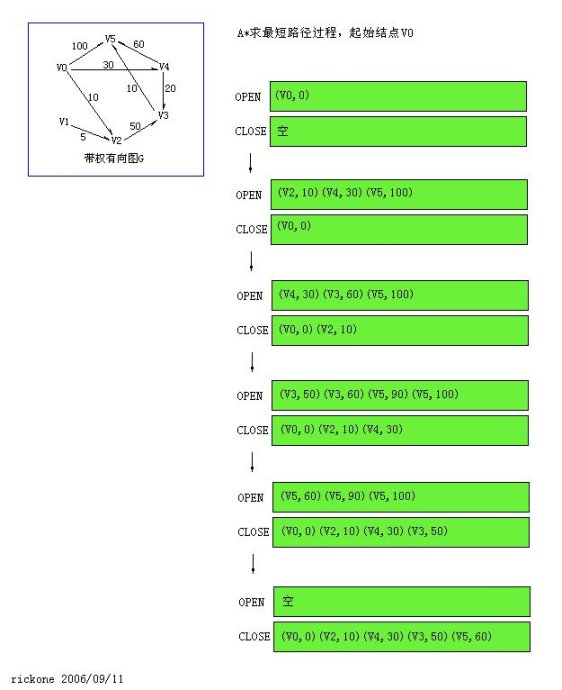
图片是引用rickone 的。上图中,说白了,无非就是: 一个队列,open 往close 插入元素。
通过上图,我们可以看出:
AA算法最为核心的过程,就在每次选择下一个当前搜索点时,是从所有已探知的但未搜索过点中(可能是不同层,亦可不在同一条支路上),选取f值最小的结点进行展开。
而所有“已探知的但未搜索过点”可以通过一个按f值升序的队列(即优先队列)进行排列。这样,在整体的搜索过程中,只要按照类似广度优先的算法框架,从优先队列中弹出队首元素(f值),对其可能子结点计算g、h和f值,直到优先队列为空(无解)或找到终止点为止。
AA算法与广度、深度优先和Dijkstra 算法的联系就在于:当g(n)=0时,该算法类似于DFS,当h(n)=0时,该算法类似于BFS。且同时,如果h(n)为0,只需求出g(n),即求出起点到任意顶点n的最短路径,则转化为单源最短路径问题,即Dijkstra算法。这一点,可以通过上面的AA搜索树的具体过程中将h(n)设为0或将g(n)设为0而得到。
AA算法流程
首先将起始结点S放入OPEN表,CLOSE表置空,算法开始时:
- 如果OPEN表不为空,从表头取一个结点n,如果为空算法失败。
- n是目标解吗?是,找到一个解(继续寻找,或终止算法)。
- 将n的所有后继结点展开,就是从n可以直接关联的结点(子结点),如果不在CLOSE表中,就将它们放入OPEN表,并把S放入CLOSE表,同时计算每一个后继结点的估价值f(n),将OPEN表按f(x)排序,最小的放在表头,重复算法,回到1。
与结点写在一起的数值表示那个结点的价值f(n),当OPEN表为空时CLOSE表中将求得从V0到其它所有结点的最短路径。
考虑到算法性能,外循环中每次从OPEN表取一个元素,共取了n次(共n个结点),每次展开一个结点的后续结点时,需O(n)次,同时再对OPEN表做一次排序,OPEN表大小是O(n)量级的,若用快排就是O(nlogn),乘以外循环总的复杂度是O(n^2 * logn),如果每次不是对OPEN表进行排序,因为总是不断地有新的结点添加进来,所以不用进行排序,而是每次从OPEN表中求一个最小的,那只需要O(n)的复杂度,所以总的复杂度为O(n*n),这相当于Dijkstra算法。
C语言实现AA算法
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#define MaxLength 100 //用于优先队列(Open表)的数组
#define Height 15 //地图高度
#define Width 20 //地图宽度
#define Reachable 0 //可以到达的结点
#define Bar 1 //障碍物
#define Pass 2 //需要走的步数
#define Source 3 //起点
#define Destination 4 //终点
#define Sequential 0 //顺序遍历
#define NoSolution 2 //无解决方案
#define Infinity 0xfffffff
#define East (1 << 0)
#define South_East (1 << 1)
#define South (1 << 2)
#define South_West (1 << 3)
#define West (1 << 4)
#define North_West (1 << 5)
#define North (1 << 6)
#define North_East (1 << 7)
typedef struct
{
signed char x, y;
} Point;
const Point dir[8] =
{
{0, 1}, // East
{1, 1}, // South_East
{1, 0}, // South
{1, -1}, // South_West
{0, -1}, // West
{-1, -1}, // North_West
{-1, 0}, // North
{-1, 1} // North_East
};
unsigned char within(int x, int y)
{
return (x >= 0 && y >= 0
&& x < Height && y < Width);
}
typedef struct
{
int x, y;
unsigned char reachable, sur, value;
} MapNode;
typedef struct Close
{
MapNode *cur;
char vis;
struct Close *from;
float F, G;
int H;
} Close;
typedef struct //优先队列(Open表)
{
int length; //当前队列的长度
Close* Array[MaxLength]; //评价结点的指针
} Open;
static MapNode graph[Height][Width];
static int srcX, srcY, dstX, dstY; //起始点、终点
static Close close[Height][Width];
// 优先队列基本操作
void initOpen(Open *q) //优先队列初始化
{
q->length = 0; // 队内元素数初始为0
}
void push(Open *q, Close cls[Height][Width], int x, int y, float g)
{ //向优先队列(Open表)中添加元素
Close *t;
int i, mintag;
cls[x][y].G = g; //所添加节点的坐标
cls[x][y].F = cls[x][y].G + cls[x][y].H;
q->Array[q->length++] = &(cls[x][y]);
mintag = q->length - 1;
for (i = 0; i < q->length - 1; i++)
{
if (q->Array[i]->F < q->Array[mintag]->F)
{
mintag = i;
}
}
t = q->Array[q->length - 1];
q->Array[q->length - 1] = q->Array[mintag];
q->Array[mintag] = t; //将评价函数值最小节点置于队头
}
Close* shift(Open *q)
{
return q->Array[--q->length];
}
// 地图初始化操作
void initClose(Close cls[Height][Width], int sx, int sy, int dx, int dy)
{ // 地图Close表初始化配置
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < Height; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < Width; j++)
{
cls[i][j].cur = &graph[i][j]; // Close表所指节点
cls[i][j].vis = !graph[i][j].reachable; // 是否被访问
cls[i][j].from = NULL; // 所来节点
cls[i][j].G = cls[i][j].F = 0;
cls[i][j].H = abs(dx - i) + abs(dy - j); // 评价函数值
}
}
cls[sx][sy].F = cls[sx][sy].H; //起始点评价初始值
// cls[sy][sy].G = 0; //移步花费代价值
cls[dx][dy].G = Infinity;
}
void initGraph(const int map[Height][Width], int sx, int sy, int dx, int dy)
{ //地图发生变化时重新构造地
int i, j;
srcX = sx; //起点X坐标
srcY = sy; //起点Y坐标
dstX = dx; //终点X坐标
dstY = dy; //终点Y坐标
for (i = 0; i < Height; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < Width; j++)
{
graph[i][j].x = i; //地图坐标X
graph[i][j].y = j; //地图坐标Y
graph[i][j].value = map[i][j];
graph[i][j].reachable = (graph[i][j].value == Reachable); // 节点可到达性
graph[i][j].sur = 0; //邻接节点个数
if (!graph[i][j].reachable)
{
continue;
}
if (j > 0)
{
if (graph[i][j - 1].reachable) // left节点可以到达
{
graph[i][j].sur |= West;
graph[i][j - 1].sur |= East;
}
if (i > 0)
{
if (graph[i - 1][j - 1].reachable
&& graph[i - 1][j].reachable
&& graph[i][j - 1].reachable) // up-left节点可以到达
{
graph[i][j].sur |= North_West;
graph[i - 1][j - 1].sur |= South_East;
}
}
}
if (i > 0)
{
if (graph[i - 1][j].reachable) // up节点可以到达
{
graph[i][j].sur |= North;
graph[i - 1][j].sur |= South;
}
if (j < Width - 1)
{
if (graph[i - 1][j + 1].reachable
&& graph[i - 1][j].reachable
&& map[i][j + 1] == Reachable) // up-right节点可以到达
{
graph[i][j].sur |= North_East;
graph[i - 1][j + 1].sur |= South_West;
}
}
}
}
}
}
int bfs()
{
int times = 0;
int i, curX, curY, surX, surY;
unsigned char f = 0, r = 1;
Close *p;
Close* q[MaxLength] = { &close[srcX][srcY] };
initClose(close, srcX, srcY, dstX, dstY);
close[srcX][srcY].vis = 1;
while (r != f)
{
p = q[f];
f = (f + 1) % MaxLength;
curX = p->cur->x;
curY = p->cur->y;
for (i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
if (! (p->cur->sur & (1 << i)))
{
continue;
}
surX = curX + dir[i].x;
surY = curY + dir[i].y;
if (! close[surX][surY].vis)
{
close[surX][surY].from = p;
close[surX][surY].vis = 1;
close[surX][surY].G = p->G + 1;
q[r] = &close[surX][surY];
r = (r + 1) % MaxLength;
}
}
times++;
}
return times;
}
int astar()
{ // AA算法遍历
//int times = 0;
int i, curX, curY, surX, surY;
float surG;
Open q; //Open表
Close *p;
initOpen(&q);
initClose(close, srcX, srcY, dstX, dstY);
close[srcX][srcY].vis = 1;
push(&q, close, srcX, srcY, 0);
while (q.length)
{ //times++;
p = shift(&q);
curX = p->cur->x;
curY = p->cur->y;
if (!p->H)
{
return Sequential;
}
for (i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
if (! (p->cur->sur & (1 << i)))
{
continue;
}
surX = curX + dir[i].x;
surY = curY + dir[i].y;
if (!close[surX][surY].vis)
{
close[surX][surY].vis = 1;
close[surX][surY].from = p;
surG = p->G + sqrt((curX - surX) * (curX - surX) + (curY - surY) * (curY - surY));
push(&q, close, surX, surY, surG);
}
}
}
//printf("times: %d\n", times);
return NoSolution; //无结果
}
const int map[Height][Width] = {
{0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1},
{0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,1},
{0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0},
{0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1},
{0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0}
};
const char Symbol[5][3] = { "□", "▓", "▽", "☆", "◎" };
void printMap()
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < Height; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < Width; j++)
{
printf("%s", Symbol[graph[i][j].value]);
}
puts("");
}
puts("");
}
Close* getShortest()
{ // 获取最短路径
int result = astar();
Close *p, *t, *q = NULL;
switch(result)
{
case Sequential: //顺序最近
p = &(close[dstX][dstY]);
while (p) //转置路径
{
t = p->from;
p->from = q;
q = p;
p = t;
}
close[srcX][srcY].from = q->from;
return &(close[srcX][srcY]);
case NoSolution:
return NULL;
}
return NULL;
}
static Close *start;
static int shortestep;
int printShortest()
{
Close *p;
int step = 0;
p = getShortest();
start = p;
if (!p)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
while (p->from)
{
graph[p->cur->x][p->cur->y].value = Pass;
printf("(%d,%d)→\n", p->cur->x, p->cur->y);
p = p->from;
step++;
}
printf("(%d,%d)\n", p->cur->x, p->cur->y);
graph[srcX][srcY].value = Source;
graph[dstX][dstY].value = Destination;
return step;
}
}
void clearMap()
{ // Clear Map Marks of Steps
Close *p = start;
while (p)
{
graph[p->cur->x][p->cur->y].value = Reachable;
p = p->from;
}
graph[srcX][srcY].value = map[srcX][srcY];
graph[dstX][dstY].value = map[dstX][dstY];
}
void printDepth()
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < Height; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < Width; j++)
{
if (map[i][j])
{
printf("%s ", Symbol[graph[i][j].value]);
}
else
{
printf("%2.0lf ", close[i][j].G);
}
}
puts("");
}
puts("");
}
void printSur()
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < Height; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < Width; j++)
{
printf("%02x ", graph[i][j].sur);
}
puts("");
}
puts("");
}
void printH()
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < Height; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < Width; j++)
{
printf("%02d ", close[i][j].H);
}
puts("");
}
puts("");
}
int main(int argc, const char **argv)
{
initGraph(map, 0, 0, 0, 0);
printMap();
while (scanf("%d %d %d %d", &srcX, &srcY, &dstX, &dstY) != EOF)
{
if (within(srcX, srcY) && within(dstX, dstY))
{
if (shortestep = printShortest())
{
printf("从(%d,%d)到(%d,%d)的最短步数是: %d\n",
srcX, srcY, dstX, dstY, shortestep);
printMap();
clearMap();
bfs();
//printDepth();
puts((shortestep == close[dstX][dstY].G) ? "正确" : "错误");
clearMap();
}
else
{
printf("从(%d,%d)不可到达(%d,%d)\n",
srcX, srcY, dstX, dstY);
}
}
else
{
puts("输入错误!");
}
}
return (0);
}参考
